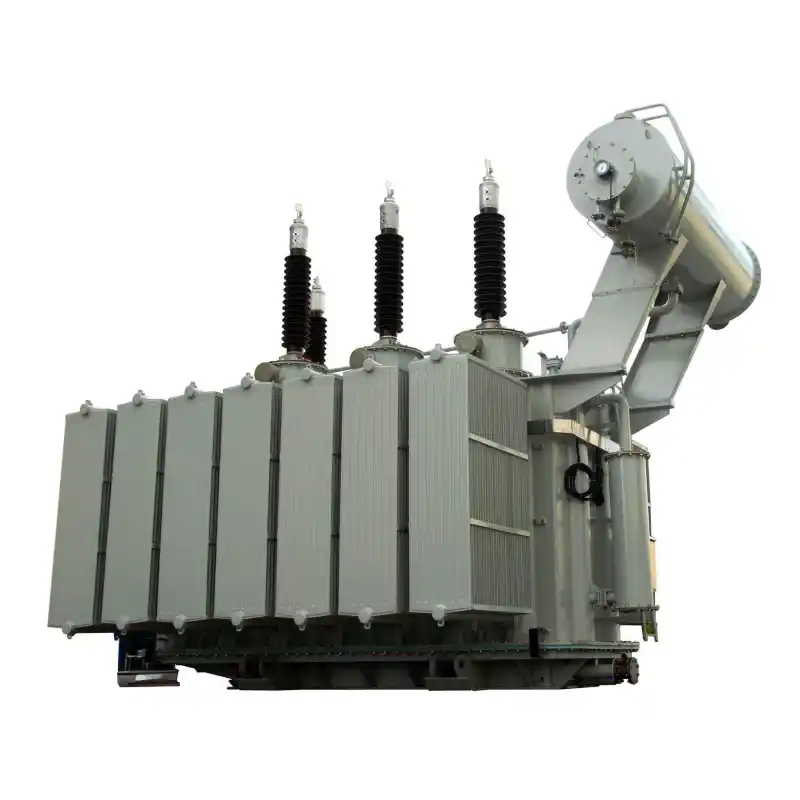
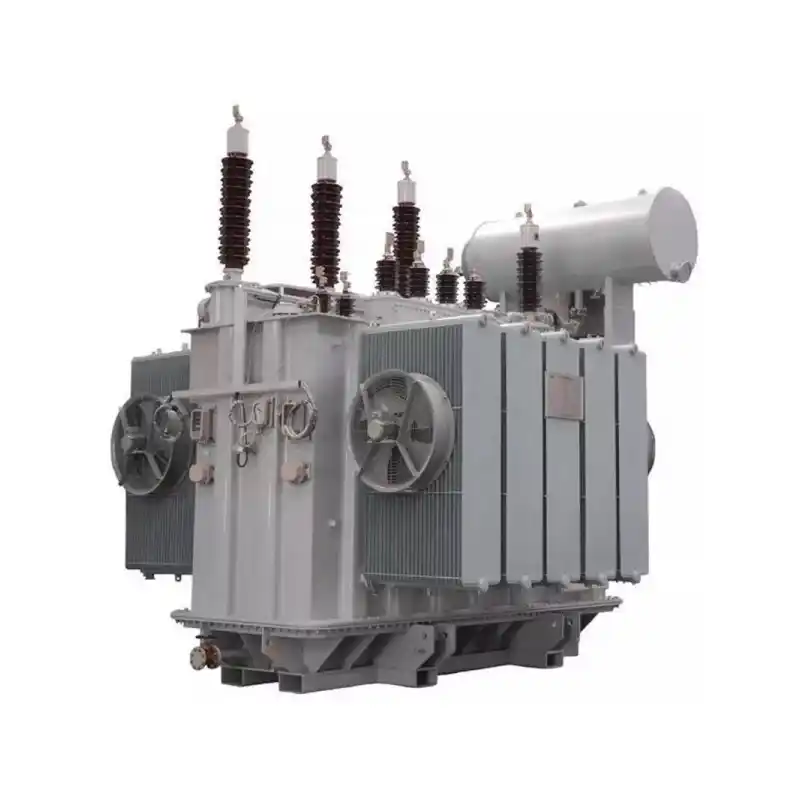
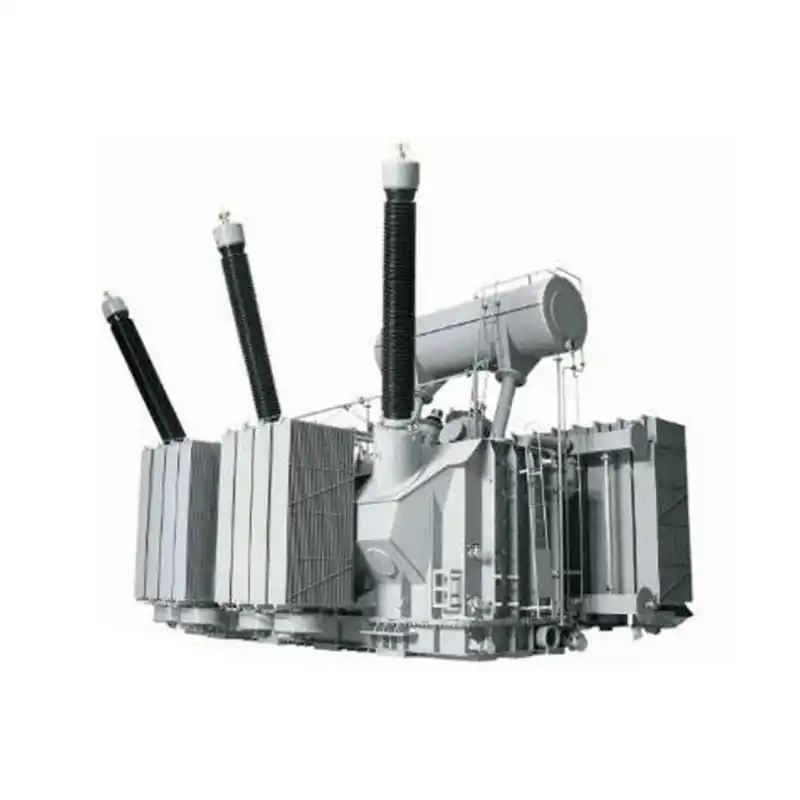
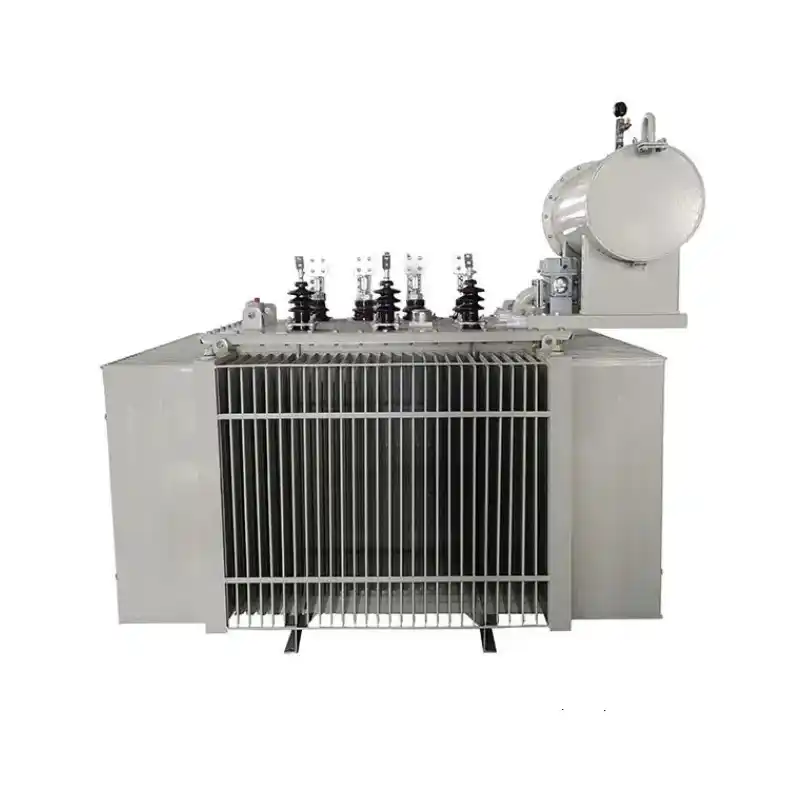
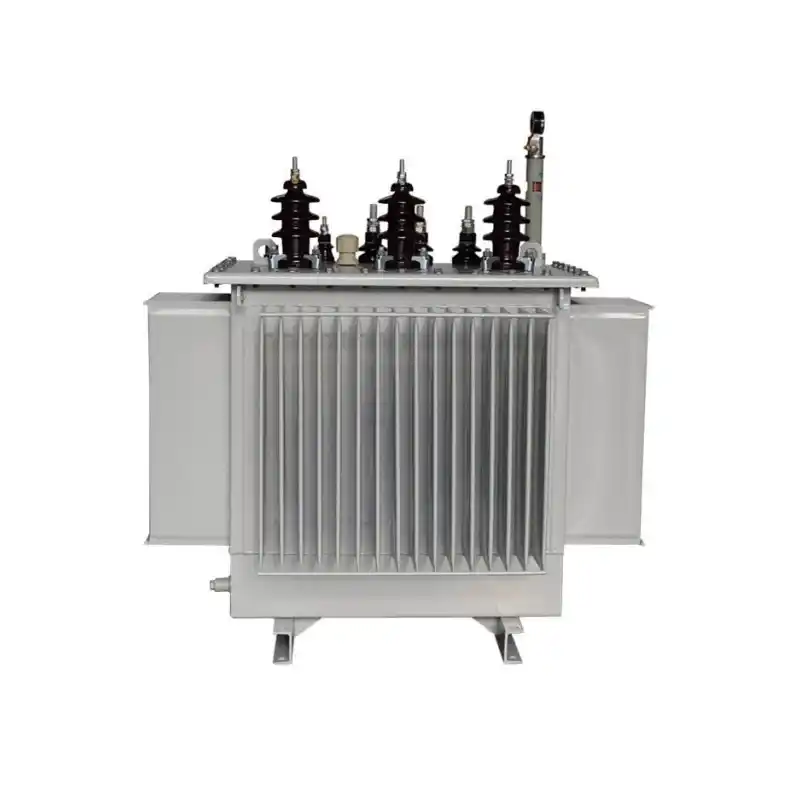
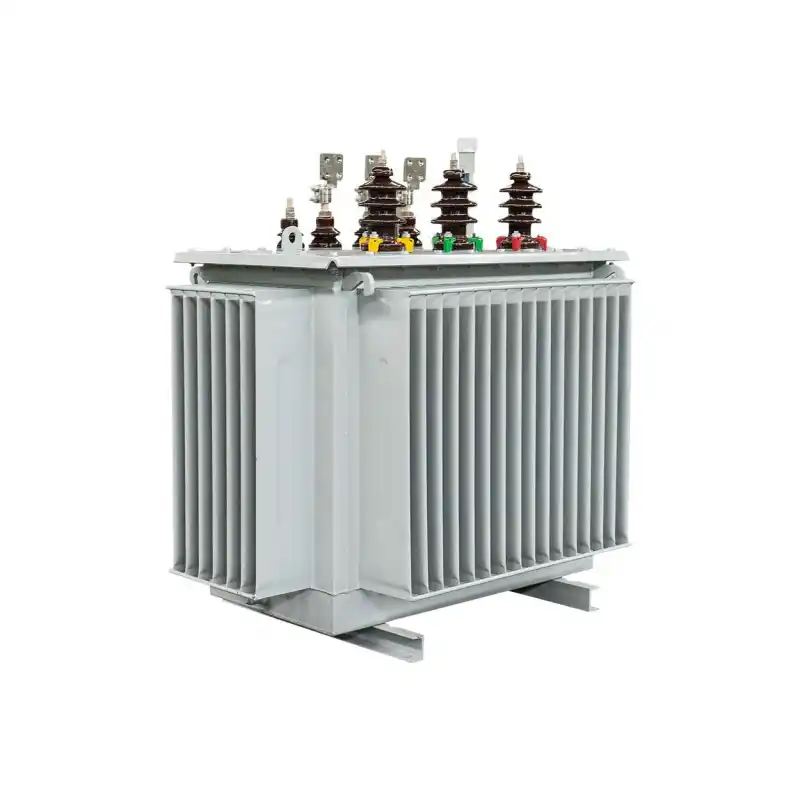
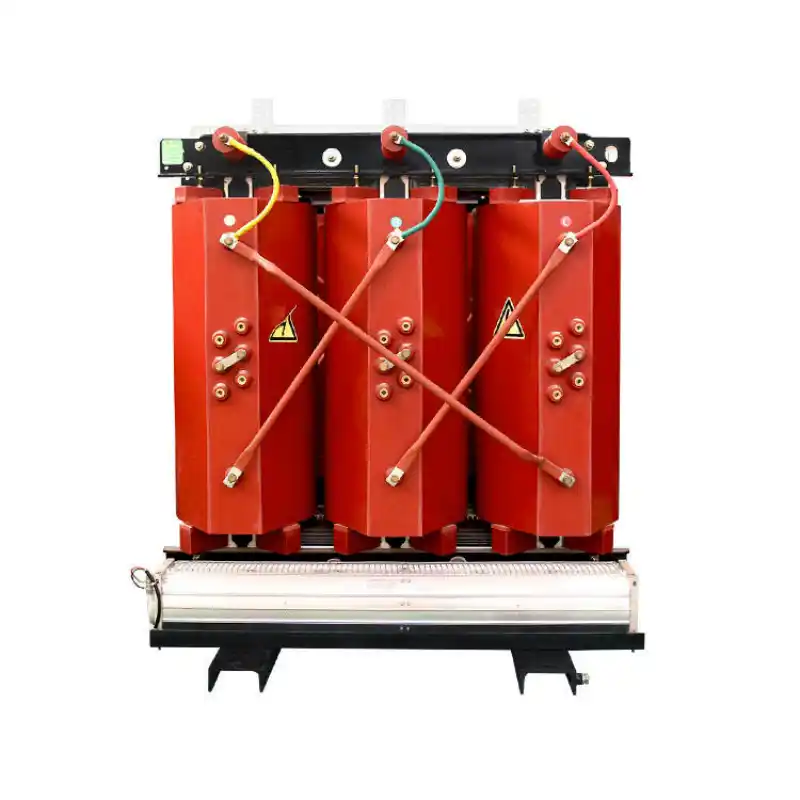
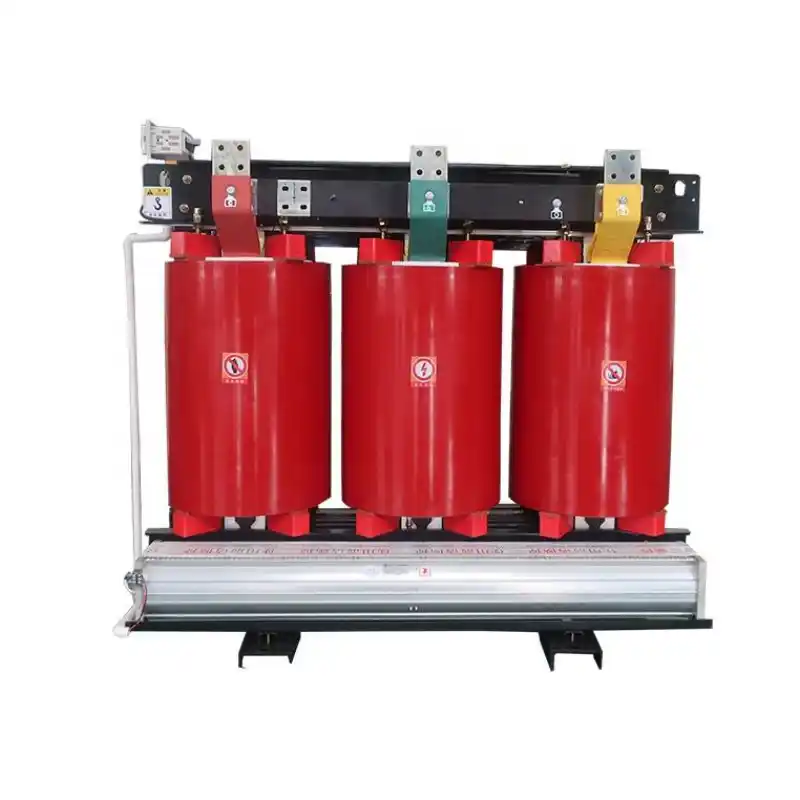
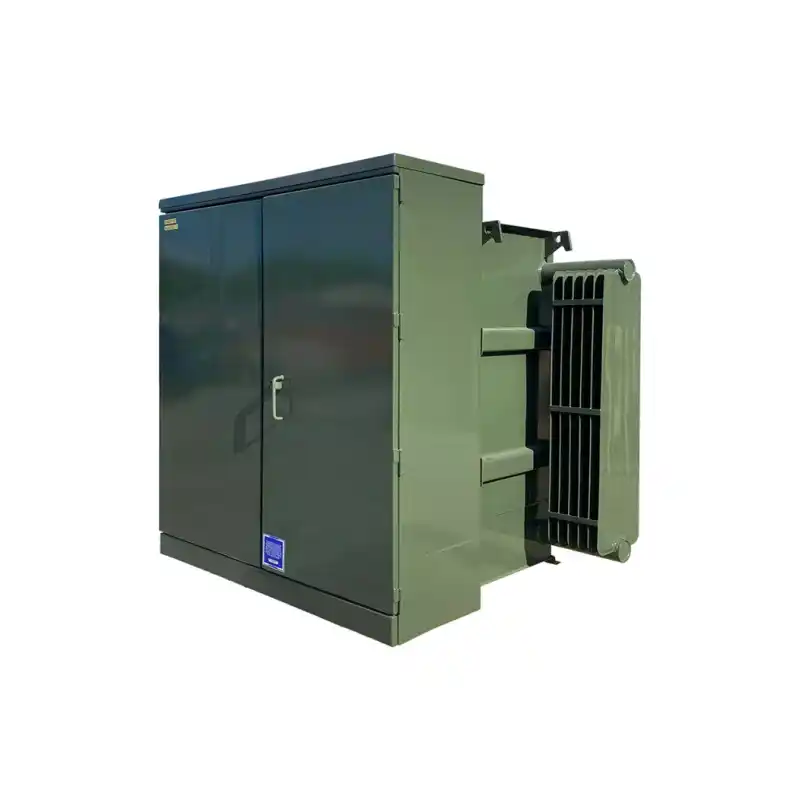
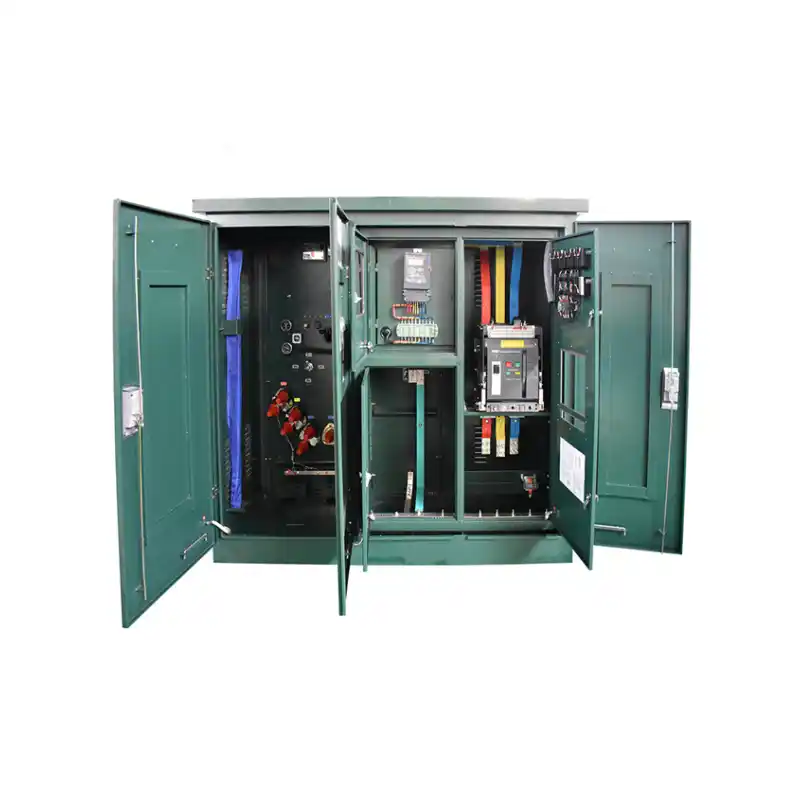
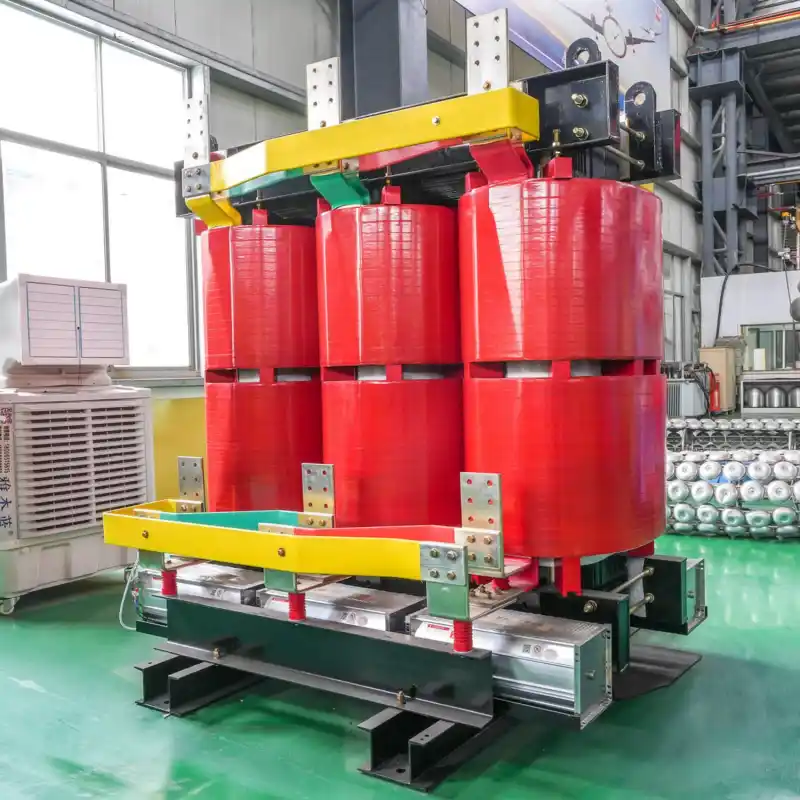
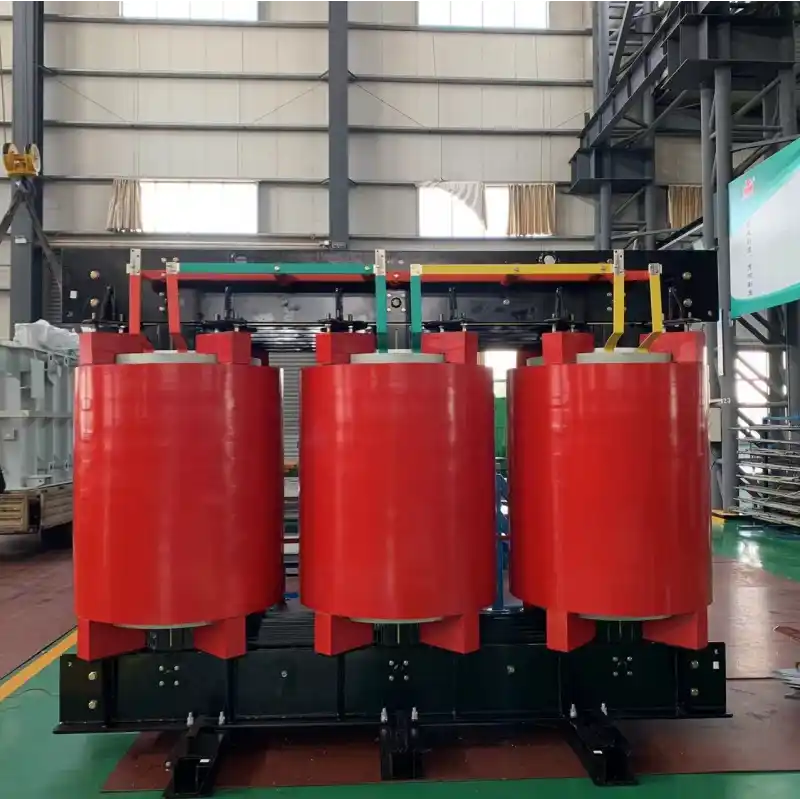
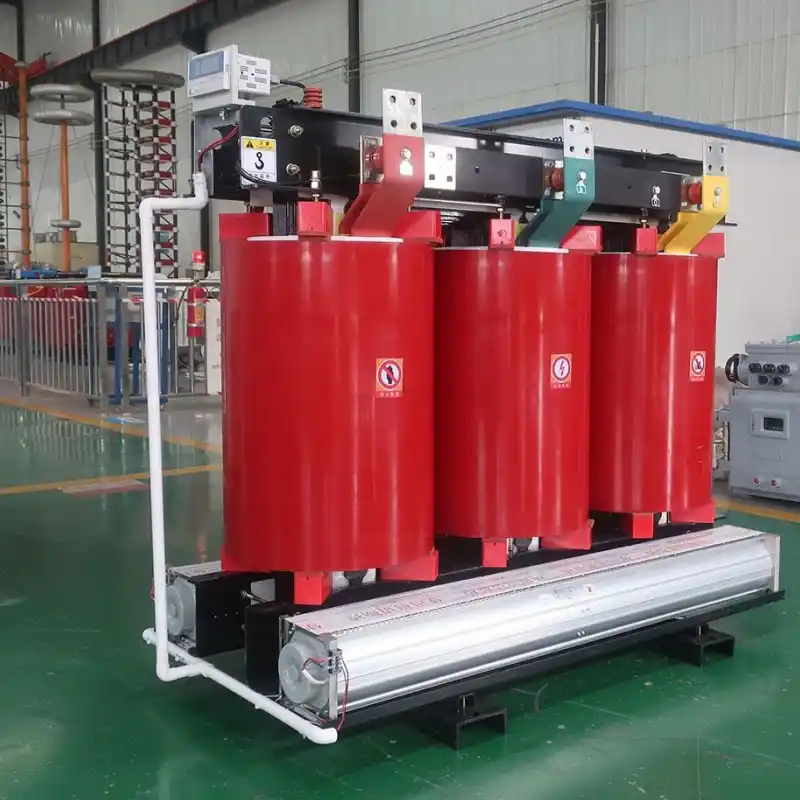
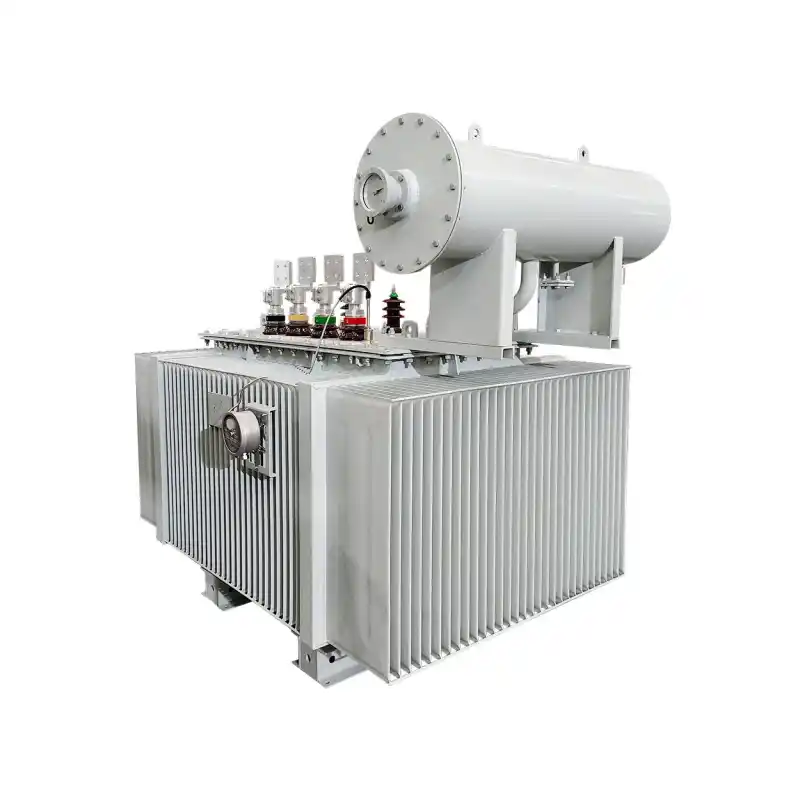
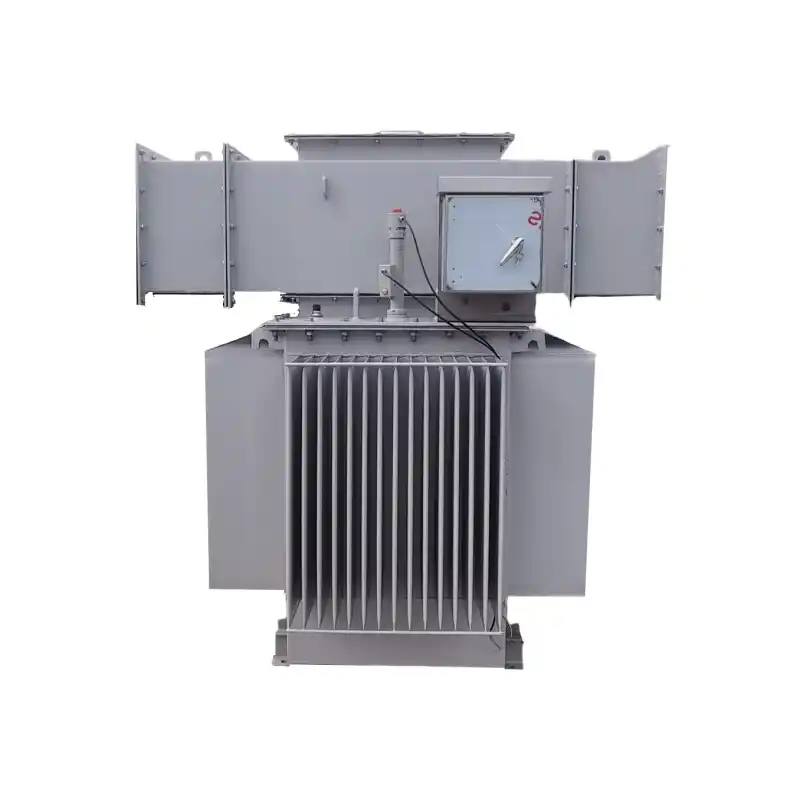
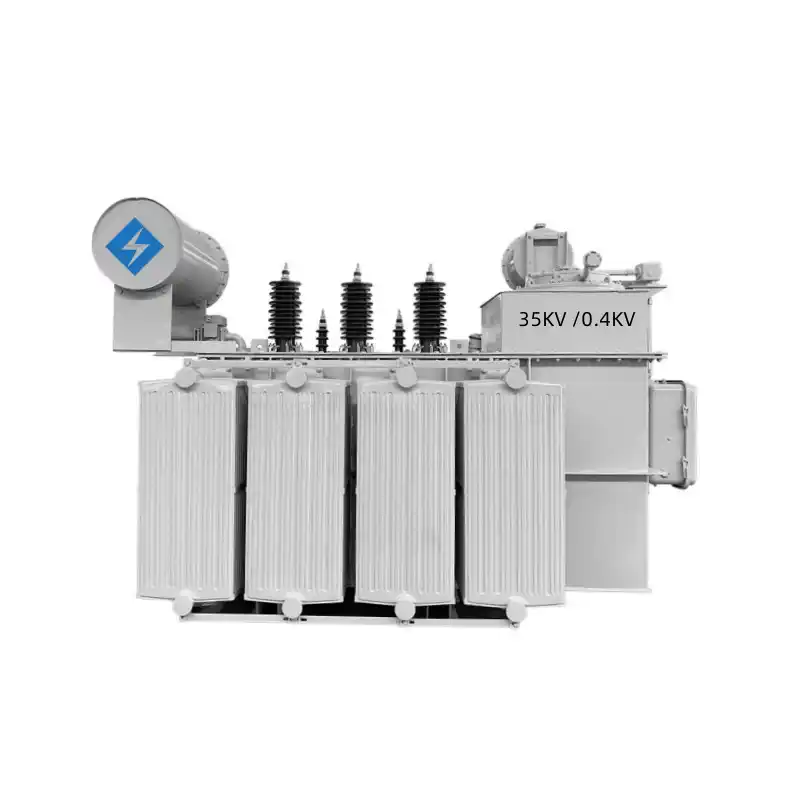
high-voltage transmission systems
In high-voltage transmission systems, transformers play a crucial role. There are two main types of transformers used in high-voltage transmission systems:
-
Step-up Transformer: 3 phase Step-up transformers are used to raise the low-voltage electrical energy generated by power plants to the high voltage levels suitable for long-distance transmission. High voltage reduces the flow of current in transmission lines, thereby minimizing energy losses. Step-up transformers are typically installed at power plants or substations to increase the voltage of generated electricity to the levels required for transmission over long distances.
-
Distribution Transformer: Distribution transformers are used to lower the voltage from high-voltage transmission systems to the low voltage levels suitable for end-users. In electrical distribution networks, distribution transformers are installed at substations and utility poles to reduce the voltage from high or medium voltage transmission lines to the low voltage levels used by homes and commercial buildings. Typically, distribution transformers are installed at distribution substations to step down the voltage from high (e.g., 110kV, 66kV) or medium (e.g., 10kV, 35kV) levels to the low voltage (e.g., 400V, 220V) levels available to users.
These transformers ensure efficient transmission and stable distribution of electrical energy in high-voltage transmission systems, thereby ensuring the safe operation and reliable supply of power in the power system.
Low-voltage Distribution Systems
In low-voltage distribution systems, transformers are essential components. There are mainly two types of transformers used in low-voltage distribution systems:
-
Step-down Transformer: Step-down transformers are used to decrease the high voltage levels from the transmission or distribution lines to the lower voltage levels suitable for end-users. These transformers are typically installed at distribution substations or utility poles to reduce the voltage from medium or high-voltage transmission lines to the levels used by residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. Step-down transformers play a crucial role in providing safe and usable voltage levels to various electrical appliances and equipment.
-
Isolation Transformer: Isolation transformers are used to provide electrical isolation between input and output circuits, thereby preventing electrical noise and disturbances from affecting the system. These transformers are particularly useful in sensitive electronic applications where electrical isolation and additional safety protection are required. Isolation transformers help to ensure the safety and reliability of electrical systems by preventing issues such as ground loops and electrical interference.
These transformers are integral to the efficient and reliable operation of low-voltage distribution systems, providing safe and stable electrical power to end-users while also protecting electrical equipment from potential hazards and disturbances.
Transmission and distribution system transformers Type:
Transformer applications in industrial systems
Application of transformer in motor drive
Transformers play a crucial role in motor drives, especially in the context of power electronics and electric motor control. Here are some applications of transformers in motor drives:
-
Isolation: Transformers are commonly used to provide galvanic isolation between different parts of a motor drive system. This isolation helps in safety, reducing noise, and preventing ground loops.
-
Voltage Transformation: In motor drives, it’s often necessary to step up or step down voltage levels to match the requirements of the motor and the power supply. Transformers facilitate this voltage transformation efficiently.
-
Impedance Matching: Transformers can be used to match the impedance between different components of the motor drive system, ensuring optimal power transfer and efficiency.
-
Filtering and Noise Reduction: Transformers can be employed in filtering circuits to reduce noise and harmonics generated by the motor drive system, thereby improving the overall performance and reliability.
-
Current Sensing: Current transformers (CTs) are used for sensing and measuring the current in motor drive systems. They provide a scaled-down version of the current flowing through a conductor, which can be easily measured and monitored.
-
Power Distribution: Transformers are used for power distribution in motor drive systems, especially in industrial applications where multiple motors are controlled from a single power source.
-
Energy Efficiency: By stepping up voltage levels for transmission and stepping down for utilization, transformers help in improving the overall energy efficiency of motor drive systems by reducing losses during power transmission.
Application of transformers in control systems
Transformers find various applications in control systems across different industries and domains. Here are some common applications:
-
Signal Isolation: Transformers are frequently used to isolate control signals from power circuits, ensuring safety and preventing interference. Isolation transformers provide galvanic isolation between control circuits and high-voltage power circuits, protecting sensitive control electronics from damage.
-
Voltage Conversion: In control systems, it’s often necessary to convert voltage levels to match the requirements of different components. Transformers facilitate this voltage conversion, stepping up or stepping down voltages as needed.
-
Instrumentation: Current transformers (CTs) and voltage transformers (VTs) are commonly used in control systems for measuring and monitoring electrical parameters such as current and voltage. They provide scaled-down representations of these parameters that can be easily processed by control circuits.
-
Power Supply: Transformers are used in power supply units of control systems to step down the voltage from the mains supply to a level suitable for powering control electronics. These transformers are often integrated into AC/DC converters or DC/DC converters to provide stable DC power.
-
Impedance Matching: Transformers are employed for impedance matching in control systems to ensure efficient transfer of signals between different components. Matching the impedance helps to minimize signal reflection and maximize power transfer.
-
Filters and Noise Reduction: Transformers can be used in filtering circuits to reduce noise and harmonics in control signals, improving the accuracy and reliability of control systems.
-
Protection Circuits: Transformers play a role in protection circuits of control systems, providing isolation and voltage scaling for monitoring and protecting against overvoltage, overcurrent, and other fault conditions.
-
Signal Conditioning: Transformers are utilized for signal conditioning in control systems, adjusting signal levels and characteristics to meet the requirements of downstream components such as sensors, actuators, and controllers.
-
Communication Interfaces: Transformers are used in communication interfaces of control systems, such as Ethernet transformers and isolation transformers in serial communication interfaces like RS-485, to provide isolation and impedance matching while transmitting data between devices.
-
Frequency Conversion: In some control systems, especially those involving power electronics and variable frequency drives, transformers are used for frequency conversion to control the speed and operation of motors and other equipment.
Overall, transformers play a critical role in enabling efficient, safe, and reliable operation of control systems across various applications and industries.
Industrial Systems Transformers Type:
Application Of Transformers In Generators
Transformers play several crucial roles in generator systems, especially in power generation and distribution. Here are some key applications of transformers in generators:
-
Voltage Transformation: Transformers are used to step up the voltage generated by the generator to higher levels suitable for efficient transmission over long distances. Higher voltages reduce the current flow, resulting in lower losses during transmission according to the equation P = I²R. This is essential for transmitting power generated at power plants to distant areas.
-
Grid Connection: Generators typically produce electricity at lower voltage levels, which need to be stepped up for connection to the power grid. Large power transformers, often located at substations, step up the voltage of electricity generated by the generators before it is fed into the transmission grid.
-
Distribution: Transformers are used to step down the high-voltage electricity from the transmission grid to lower voltage levels suitable for distribution to end-users. Distribution transformers located on utility poles or in substations further reduce the voltage to levels appropriate for residential, commercial, and industrial consumption.
-
Isolation and Grounding: Transformers provide isolation between the generator and the power grid or distribution system. This isolation protects both the generator and the grid from potential faults or disturbances that may occur on either side. Additionally, transformers help in grounding the system, ensuring safety and mitigating the risk of electrical shocks.
-
Reactive Power Compensation: Transformers, particularly in conjunction with capacitor banks, are used for reactive power compensation in generator systems. This helps to improve power factor, reduce losses, and enhance the efficiency of the overall system.
-
Generator Voltage Control: Transformers can be used to regulate the voltage output of generators, especially in systems where the load fluctuates significantly. Voltage regulators, often integrated with transformers, adjust the transformer taps to maintain a stable voltage output within the desired range.
-
Backup Power Systems: In situations where generators are used as backup power sources, transformers may be employed to match the voltage and phase of the generator output with that of the main power supply, ensuring seamless transfer of power during grid outages.
-
Harmonic Filtering: Transformers with harmonic filters can be used to mitigate the effects of harmonics generated by non-linear loads connected to the generator system. These filters help in improving the quality of power supplied to sensitive equipment and reducing the risk of equipment malfunction or damage.
In summary, transformers are indispensable components in generator systems, facilitating voltage transformation, grid connection, distribution, isolation, voltage control, and various other functions essential for efficient and reliable power generation and delivery.
Generators Systems Transformers Type:
Generators Systems Transformers Type:
Transformers play several important roles in transportation systems, especially in the context of electrical systems powering various types of vehicles and supporting infrastructure. Here are some key applications of transformers in transportation.
1. Electric Traction Systems: In electric trains, trams, and subway systems, transformers are used to step down the high-voltage AC power from overhead lines or third rails to lower voltages suitable for traction motors. These traction transformers provide the necessary voltage levels for efficient operation of the electric propulsion systems.
2. Electric Vehicles (EVs) Charging Stations: Transformers are integral components of EV charging stations, where they step down the voltage from the utility grid to the lower voltage levels required for charging the batteries of electric vehicles. Charging station transformers help ensure safe and reliable charging of EVs at various locations, including homes, workplaces, and public charging stations.
3. Railway Electrification Substations: In electrified railway systems, substations along the track supply power to trains through overhead wires or third rails. Transformers within these substations step down the high-voltage AC power from the grid to the voltages required for train propulsion, lighting, and auxiliary systems.
4. Power Distribution Systems: Transformers are used in power distribution systems supporting transportation infrastructure, such as airports, seaports, and railway stations. These transformers step down the high-voltage power from the utility grid to lower voltages suitable for lighting, HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), escalators, elevators, and other electrical loads.
5. Auxiliary Power Systems: Transformers are employed in auxiliary power systems of transportation vehicles, such as ships, airplanes, and trains, to step down the voltage from onboard generators or power sources to levels suitable for powering auxiliary equipment, lighting, HVAC, and other onboard systems.
6. Electric Bus Charging Infrastructure: In electric bus fleets, charging infrastructure requires transformers to step down the voltage from the grid to levels compatible with the charging equipment installed at bus depots or charging stations. These transformers enable the efficient charging of electric buses to support public transportation systems.
7. High-Speed Rail Systems: In high-speed rail systems, transformers are utilized to step down the voltage from the overhead catenary wires or power rails to the levels required by the train’s propulsion and auxiliary systems. Transformers help maintain the reliability and efficiency of high-speed trains by delivering stable power supply.
Overall, transformers are essential components of transportation systems, supporting electrification, power distribution, and auxiliary power requirements across various modes of transportation, including trains, trams, electric vehicles, ships, airplanes, and public transit systems.