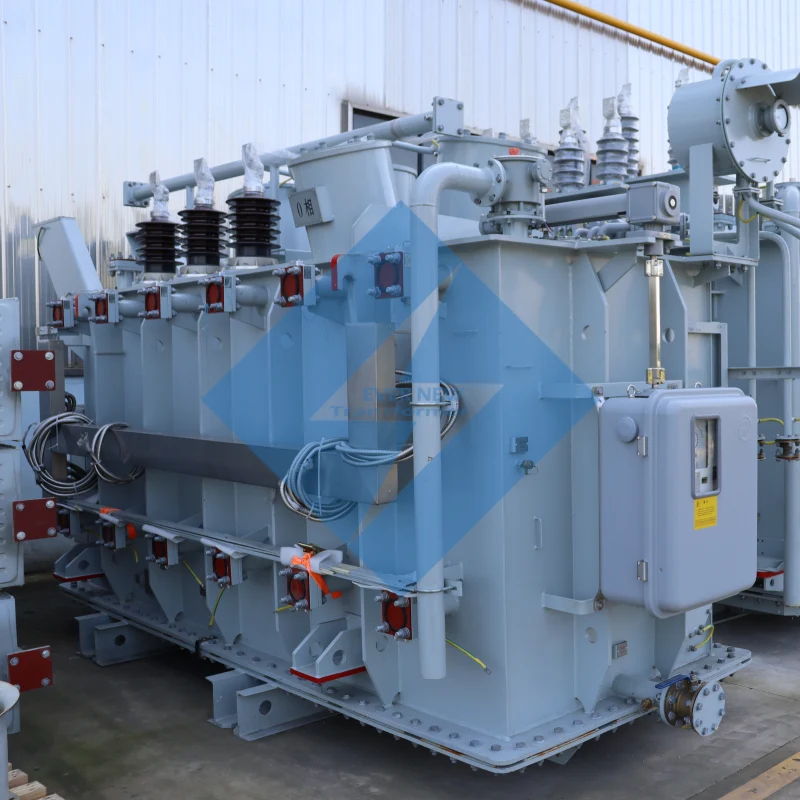
Understanding Power Plant Transformers: Types, Functions, and Applications
A power plant transformer is a critical component in any power generation facility, responsible for stepping up or stepping down the voltage to match the required levels for safe and efficient power transmission. Whether the power plant is coal-fired, nuclear, or utilizing renewable energy sources like wind or solar, transformers ensure that electrical energy can be transmitted without significant losses over long distances.
In this article, we will explore various types of power plant transformers, their parameters, functions, and applications, and highlight how Evernew Transformer, a leading transformer manufacturer in China, plays a pivotal role in producing reliable and efficient transformers for power plants worldwide.
Power Plant Transformers: Role and Functions
A power plant transformer serves a fundamental role in converting the voltage generated by power plants to suitable levels for transmission and distribution. Typically, the power plant’s generator produces electricity at low voltages (e.g., 10-25 kV), which must be stepped up (or stepped down) to the appropriate voltage (ranging from 110 kV to 765 kV) for long-distance transmission. This step-up transformation reduces the current and minimizes losses across the grid.
The voltage levels generated by power plants are too high for safe use by consumers, requiring a power plant transformer to step down voltage levels, depending on the application—whether for distribution to local areas or for internal power consumption within the plant.
Key Transformer Parameters
Understanding the technical parameters of power plant transformers is essential for selecting the right model for each type of power plant. Here are key parameters to consider:
- Rated Power (kVA or MVA): The transformer’s capacity to handle electrical loads, usually specified in kilovolt-amperes (kVA) or megavolt-amperes (MVA). Larger power plants may require transformers in the range of 100 MVA to over 1000 MVA.
- Primary Voltage: This refers to the voltage level of the electricity supplied to the transformer (e.g., 10 kV to 25 kV from the generator).
- Secondary Voltage: This is the voltage level output by the transformer, which could range from 110 kV to 765 kV, depending on the application (e.g., for transmission to the grid).
- Impedance: Impedance affects the voltage regulation and short-circuit current capabilities of the transformer. Transformers for power plants typically have low impedance values to maintain high efficiency.
- Cooling Method: Common cooling methods for power plant transformers include oil cooling (ONAN, ONAF, OFAF) and natural air cooling (AN), which help manage the heat generated during energy conversion.
- Efficiency: A high-efficiency transformer minimizes energy loss during the conversion process, which is crucial in large-scale power plants.
- Tap Changer: Some transformers are equipped with tap changers to adjust the voltage output dynamically based on load fluctuations.
These parameters vary depending on the type of power plant and the specific role the transformer will play, whether it is a step up transformer for voltage increase or a step down transformer for voltage reduction.
Read More:220 kv 230kv High Voltage Special Oil Immersed Power Transformer
Contact Us Now
Types of Power Plant Transformers
Depending on the type of power plant and the specific requirements, several types of transformers are used. Each has unique parameters and applications.
Step-Up Transformers
Step-up power plant transformers are crucial for increasing the voltage generated by the plant’s generator to the required level for transmission across the grid. The rated power of step up transformers can range from tens of MVA to several hundred MVA, depending on the scale of the power generation. The high voltage output typically ranges from 110 kV to 765 kV.
Applications:
- Coal Power Plants: Step up transformers in coal fired plants convert the lower voltage produced by generators (typically around 15 kV) to much higher transmission voltages.
- Nuclear Power Plants: In nuclear plants, step-up transformers increase the voltage produced by nuclear reactors to high levels, making them suitable for grid transmission.
Read More:63kv 66kv 69kv High Voltage Power Transformer Manufacturer
Step Down Transformers
Step down power plant transformers are used to lower the voltage of the electricity after it has been transmitted through long distance lines, ensuring safe and efficient distribution to consumers. These transformers typically handle lower voltages (e.g., from 110 kV to 11 kV) and can be found in substations.
Applications:
- Renewable Energy Plants: In solar and wind farms, step down transformers reduce the high voltage power from the turbine or solar array to a usable level for local distribution.
- Combined Cycle Power Plants: These plants use step down transformers to reduce the voltage before sending electricity to local distribution systems.
Auxiliary Transformers
Auxiliary power plant transformers provide power to auxiliary systems within the power plant. These transformers often handle low voltage levels and are crucial for keeping plant operations running, including lighting, control systems, and cooling.
Applications:
- Hydroelectric Plants: Auxiliary transformers provide power to pumps, control systems, and safety equipment.
- Geothermal Power Plants: These transformers ensure that geothermal plants operate smoothly by powering the plant’s internal systems.
Generator Transformers
These transformers directly connect to the generator, transforming its electrical output to match the voltage levels required for the grid. Generator transformers are designed to handle the higher electrical outputs produced by the generator, with some having ratings in excess of 100 MVA.
Applications:
- Gas Turbine Power Plants: These plants use generator transformers to connect the high voltage electricity produced by turbines to the grid.
- Wind Power Plants: Generator transformers connect the power generated by turbines to the local or national grid.

Contact Us Now
Importance of Power Plant Transformers Across Different Types of Power Plants
The type of power plant transformer used depends largely on the nature of the power generation process and the specific needs of the plant. For example, coal, nuclear, and gas turbine plants require heavy duty step up transformers, while renewable energy plants often require step down transformers to manage the electricity for local use.
Coal Power Plants
Step-up transformers in coal power plants increase the generated voltage from the plant’s generators to a suitable level for transmission. Due to the large-scale energy production, these transformers are typically large, handling capacities of 100 MVA and above.
Nuclear Power Plants
Similar to coal plants, nuclear power plants require step up transformers to increase voltage for long-distance transmission. These transformers are built with stringent safety standards due to the high stakes of nuclear energy generation.
Contact a technical expert to learn more about power plant transformers
Renewable Energy Plants
Renewable energy plants often employ step up and step down transformers in combination to manage the conversion of energy from turbines, solar panels, or hydroelectric generators. Evernew Transformer, a leading manufacturer, offers custom made transformers specifically designed to integrate seamlessly into solar, wind, and hydro plants.
Gas and Combined Cycle Power Plants
Gas turbine and combined cycle plants use generator transformers to connect the power generated from turbines to the electrical grid. The voltage output from these generators can be high, necessitating robust and efficient transformer solutions.
Hydroelectric Plants
In hydroelectric plants, step down transformers ensure that the power produced is reduced to safe levels for local distribution. Additionally, auxiliary transformers are essential for powering the plant’s operational systems, such as turbine controls and monitoring systems.
Read More:33/0.48KV 5000 KVA Oil Immersed Substation Transformer

Contact Us Now
Power transformers are the heart of power plants, ensuring the efficient transmission of electricity at the required voltage levels. Selecting the right transformer is crucial for optimizing performance, enhancing system reliability, and minimizing costs. In this article, we will discuss the key factors to consider when choosing power transformers for power plants, with insights from Evernew Transformer, a leading manufacturer of power transformer.
Determining the Number of Phases
The first step in selecting a power transformer is deciding between single-phase and three-phase transformers. While both types are available, three-phase transformers are generally preferred for power plants due to their cost-effectiveness, compact size, and lower losses.
- Three-Phase Transformers: These are typically used in systems below 330kV because they offer reduced costs and enhanced efficiency compared to single-phase transformers.
- Single-Phase Transformers: Although less common in large power plants, single-phase transformers are sometimes used when manufacturing or transportation constraints limit the use of three-phase transformers. However, this is an exception rather than the rule.
For most power plants, selecting a three-phase transformer is the most economical and practical choice.
Choosing the Right Transformer Windings
The number of windings in a transformer plays a significant role in determining its voltage regulation and operational flexibility. Transformers can come with multiple winding options, including three-winding, dual-winding, autotransformers, and split-winding designs.
- Three-Winding Transformers: Typically used when a power plant has a maximum single-unit capacity of 125MW or less, these transformers allow a more efficient integration of the generator and electrical network.
- Dual-Winding Transformers: For plants where only a single voltage level needs to be increased, dual-winding transformers are the most common choice, especially when the plant’s capacity exceeds 200MW.
- Autotransformers: These are economically advantageous, particularly in systems where the voltage ratio is relatively low. However, the design needs careful consideration, as autotransformers involve electrical connections between different voltage levels, which can lead to potential overvoltage issues. For plants with voltage levels above 220kV, autotransformers are commonly selected.
Read More:3000 KVA Pad Mounted Transformer
Choosing the Tap Changer (Voltage Regulation)
Transformers are equipped with tap changers that allow for adjustments to the voltage levels. There are two primary types of tap changers: on-load tap changers (OLTC) and off-load tap changers (OLTC).
- On-Load Tap Changers: These allow voltage adjustment while the transformer is under load and are commonly used in power plants where voltage stability is critical.
- Off-Load Tap Changers: Used when the transformer is not under load, these are generally more economical and simpler but offer less flexibility for dynamic voltage regulation.
If a power plant experiences significant voltage fluctuations or operates in areas with fluctuating load conditions, an on-load tap changer is the preferred choice.
Choosing the Correct Winding Connection
The connection method of transformer windings must be selected based on system voltage phases and compatibility. The common configurations include star (Y) and delta (D) connections.
- Star Connection (Y): Typically used for high-voltage windings, star connections provide a neutral point for easy connection to the electrical grid. This configuration helps eliminate third-order harmonics and allows for simpler protection systems.
- Delta Connection (D): Often used on the low-voltage side, delta connections prevent zero-sequence currents and offer protection against phase imbalances.
For power plants, choosing the correct connection ensures that the transformer can operate efficiently and integrate seamlessly with the power grid. Typically, for 110kV and higher voltage levels, the Y-N connection is standard, while for voltages below 110kV, the Y-y connection is preferred.
Read More:2500 KVA Three Phase Pad Mounted Transformer
Transformer Impedance Selection
Transformer impedance plays a crucial role in determining how a transformer will perform under short-circuit conditions and its overall impact on the power system. Transformer impedance is directly related to its design and the positioning of windings relative to the core.
- Higher Impedance: A higher impedance transformer will help reduce the amount of short-circuit current and enhance system stability.
- Lower Impedance: A lower impedance transformer, on the other hand, reduces system losses but can lead to higher short-circuit currents, potentially complicating protection strategies.
For power plants, selecting the appropriate impedance is critical for ensuring safe operation and stability during both normal and fault conditions.

Contact Us Now
Choosing the Right Transformer Type for Different Power Plants
The type of transformer used can vary based on the specific requirements of the power plant. As renewable energy sources like solar and wind power become more prominent, specialized transformers are increasingly required.
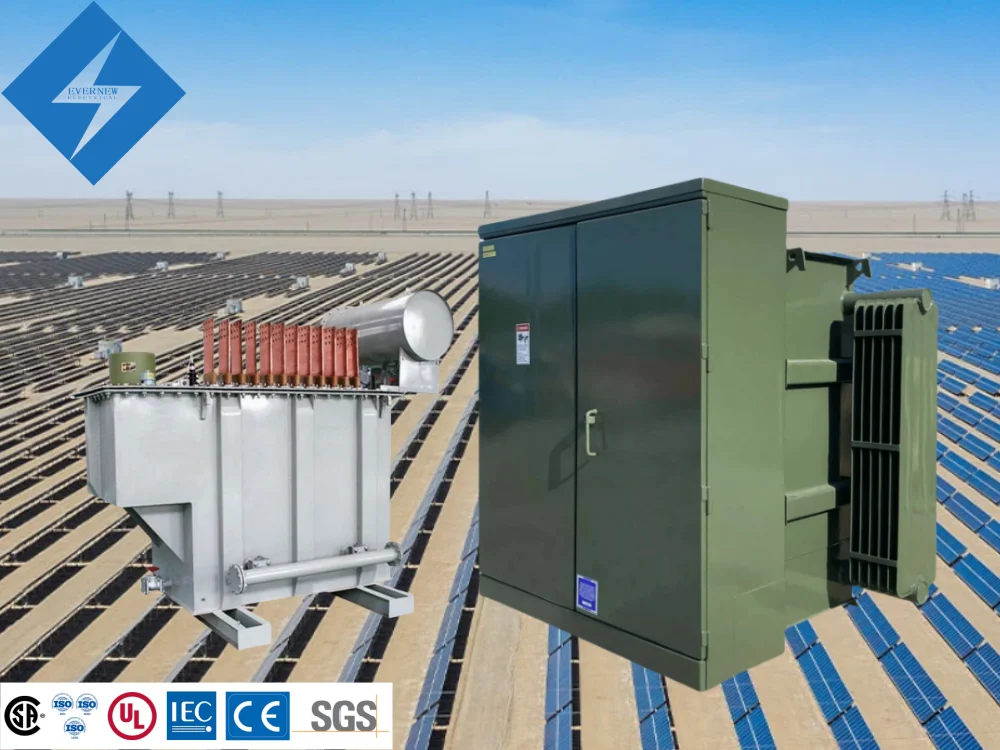
- Dry Type Transformers: Commonly used in solar power plants, these transformers do not use oil for cooling and are therefore safer and more environmentally friendly. They are typically used as isolation transformers and offer benefits such as fire resistance and minimal maintenance.
- Oil Immersed Transformers: These transformers use mineral oil for cooling and are widely used in large power plants and substations. They offer high efficiency and are capable of handling larger power capacities.
- Box Type Transformers: Used in wind and solar power plants, these compact and durable transformers are easy to install and occupy less space compared to traditional transformers.
In renewable energy projects, dry-type transformers and box-type transformers are preferred for their safety features and reduced environmental impact.
Choosing a Reliable Power Transformer Manufacturer
Power transformers play a critical role in the reliability and efficiency of a power plant, making the selection of a trustworthy manufacturer a key decision. Evernew Transformer, based in Nantong, China, is a leading manufacturer known for producing a range of high quality, efficient power transformers. With years of experience across various applications, including high-voltage substations and renewable energy projects, Evernew Transformer is dedicated to providing durable, high performance transformers.
Why Choose Evernew Transformer?
Tailored Solutions: Evernew Transformer designs custom transformers to meet specific project requirements, ensuring that each solution is perfectly suited to your operational needs.
Global Expertise: With transformers built to meet international standards and certifications, Evernew Transformer ensures seamless integration with power grids worldwide, helping clients across the globe achieve reliable power distribution.
Advanced Technology: We incorporate the latest innovations in transformer design and manufacturing, ensuring superior performance, longer lifespan, and minimal maintenance.
The Importance of International Experience and Certifications
Different markets have specific standards and certifications. While some manufacturers may perform well in local markets, a manufacturer aiming to supply high-quality power transformers for international customers must have extensive experience in the global energy market. This includes having a professional team of design, protection, and testing engineers to ensure compliance with various international requirements.
Evernew Transformer has been actively serving markets across the United States, Canada, Latin America, South America, Australia, Asia, and Africa. Thanks to our skilled engineering team and robust manufacturing processes, Evernew transformers have earned a wide range of certifications and approvals. These include:
- CSA Listing Test
- UL Listing Test
- IEC Type Testing
These certifications and testing reports help Evernew Transformer build trust with our clients and partners, ensuring that our products meet international standards and perform reliably in diverse operating environments.
Third-Party Inspection and Testing
In addition to our in-house testing and quality control, Evernew Transformer works closely with third-party inspection companies like BV, SGS, and Asia IBS to provide additional layers of verification for our products. These third-party reports further strengthen the reliability of our transformers, particularly in markets such as the United States and Canada, where regulatory compliance is critical.
With these comprehensive quality assurance processes and third-party certifications, Evernew Transformer is quickly becoming a trusted name in the international transformer market, especially in regions like North America, where reliability and adherence to stringent standards are paramount.
Conclusion: The Role of Power Plant Transformers in Efficient Energy Transmission
Transformers are at the heart of every power plant, ensuring the efficient conversion and transmission of electrical energy. From step up transformers that enable high voltage transmission to step down transformers that ensure safe local distribution, each transformer type plays a crucial role in maintaining grid stability and minimizing transmission losses.
As a trusted transformer manufacturer, Evernew Transformer offers a wide range of transformers, including step up, step down, generator, and auxiliary transformers, designed to meet the specific needs of power plants worldwide. With years of expertise and cutting edge technology, Evernew Transformer provides high efficiency transformers that maximize energy output and minimize operational costs, making them an ideal partner for power plant projects globally.

