Transformátory jsou důležitými součástmi moderních distribučních a přenosových soustav, které zajišťují bezpečnou a efektivní dodávku elektřiny v celé síti. Ať už v rozvodnách, průmyslových závodech, komerčních zařízeních nebo projektech obnovitelných zdrojů energie, transformátory plní základní úlohu zvyšování nebo snižování napětí tak, aby odpovídalo požadavkům různých fází elektrické sítě.
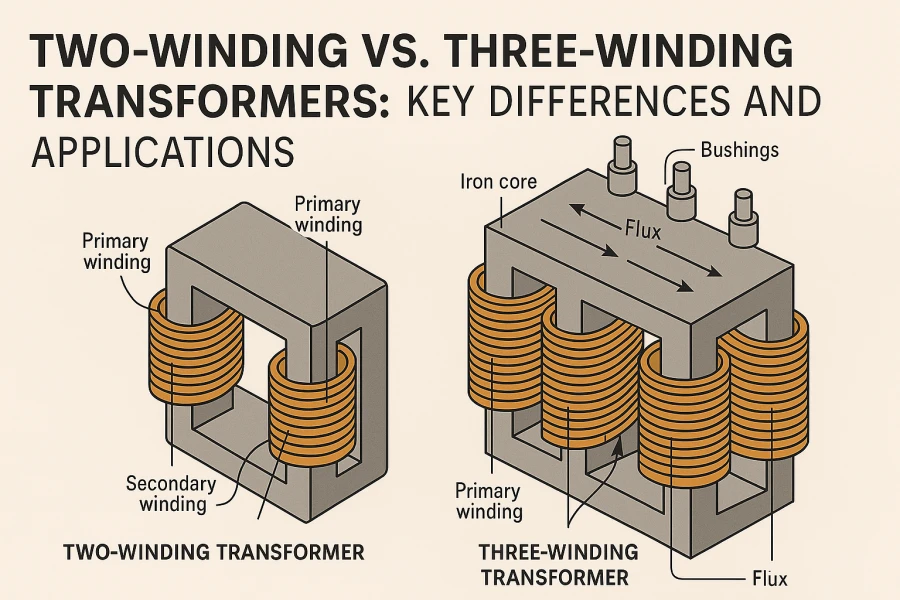
Mezi nejpoužívanější konfigurace patří dvouvinuté a třívinuté transformátory - dva základní typy, které nabízejí odlišné výhody pro energetické systémy různé složitosti. Dvouvinuťové transformátory, někdy označované jako transformátory s jedním výstupem, mají primární a sekundární vinutí, takže jsou ideální pro jednoduchou přeměnu napětí v malých až středně velkých sítích. Naproti tomu třízávitové transformátory, vybavené primárním, sekundárním a terciárním vinutím, poskytují větší flexibilitu a kapacitu zpracování výkonu, což jim umožňuje podporovat více napájecích zdrojů, vyrovnávat nerovnoměrné zatížení a zlepšovat celkovou stabilitu sítě.
Pochopením klíčových rozdílů, technických vlastností a typických aplikací těchto dvou typů transformátorů - včetně jejich účinnosti, půdorysné plochy, konfigurace vinutí a nákladů - mohou elektrotechnici, energetické společnosti a vývojáři obnovitelných zdrojů energie činit informovaná rozhodnutí, která zvýší spolehlivost systému a optimalizují dodávky energie. Ať už hledáte transformátor pro integraci do solární elektrárny, komerčního zařízení, rozvodny větrné farmy nebo distribuční sítě, znalost toho, které provedení vyhovuje vašim technickým požadavkům, zajistí dlouhodobou výkonnost a nákladovou efektivitu.
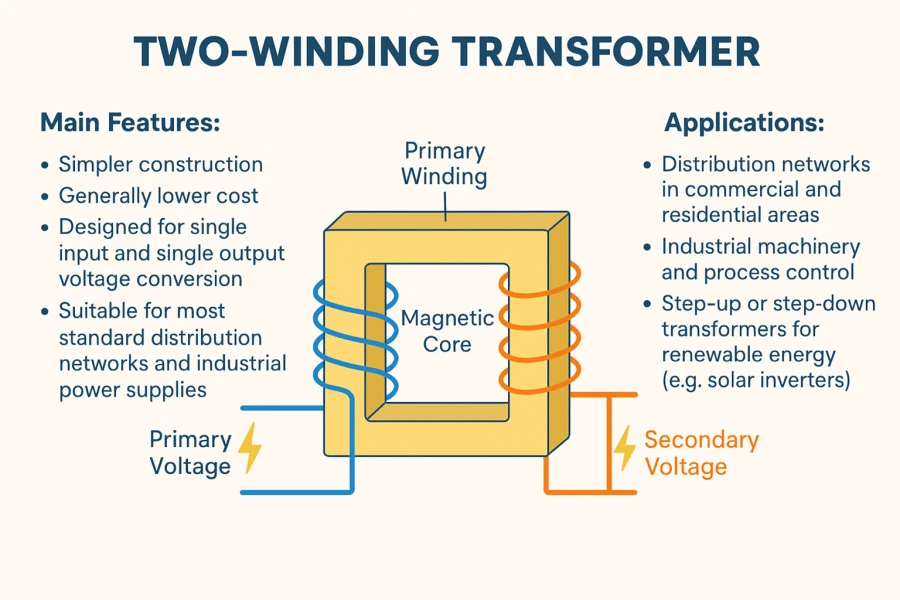
Co je dvouvinutý transformátor?
A dvouvinuťový transformátor je nejtradičnější a nejrozšířenější konstrukcí transformátoru v celém energetickém průmyslu. Obsahuje primární vinutí a sekundární vinutí, obě ovinutá kolem společného magnetického jádra. Obě vinutí přenášejí energii výhradně prostřednictvím elektromagnetické indukce a podle potřeby zvyšují nebo snižují napětí, aby vyhovovala různým stupňům rozvodu energie.
🔧 Klíčové vlastnosti:
Jednodušší struktura - osvědčená konstrukce s menším počtem komponentů a jednoduchou montáží
Nákladově efektivní řešení - nižší náklady na výrobu a údržbu
Konverze s jedním vstupem a jedním výstupem - ideální pro standardní transformaci napětí jedna ku jedné
Kompaktní půdorys - snadná integrace do většiny energetických systémů.
Vysoká spolehlivost a dlouhá životnost - osvědčený výkon v různých prostředích
Aplikace dvouvinuťových transformátorů:
Dvouvinuťové transformátory jsou základem většiny konvenčních energetických systémů a lze je nalézt v celé řadě odvětví, včetně:
Distribuční sítě veřejných služeb slouží komerčním a obytným čtvrtím
Těžké průmyslové stroje a řízení procesů ve výrobě a výrobních linkách
Středněnapěťové zvyšovací nebo snižovací transformátory pro obnovitelné zdroje energie, jako je integrace solární a větrné energie.
Veřejná infrastruktura, jako jsou železniční trakční systémy a sítě pouličního osvětlení.
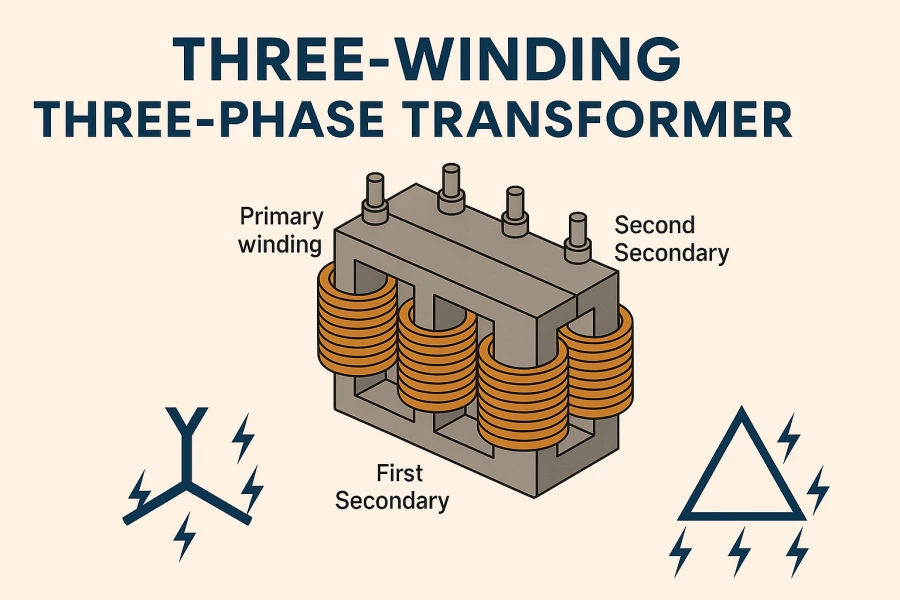
Co je to transformátor se třemi vinutími?
A transformace tří vinutír jde ještě o krok dále a k primárnímu a sekundárnímu vinutí přidává třetí vinutí, často nazývané terciární. Tato pokročilá konstrukce umožňuje transformátoru obsluhovat více výstupních napětí a napájet několik zátěží současně a zároveň zlepšuje kvalitu energie, snižuje ztráty a zvyšuje stabilitu systému.
🔧 Klíčové vlastnosti:
Zvládá více napětí - může dodávat dvě různá sekundární napětí pro různé zátěže.
Zlepšená schopnost sdílení energie - účinnější přenos energie mezi různými částmi sítě.
Vyrovnává nevyvážené zatížení - podporuje třífázové vyrovnávání zátěže a snižuje harmonické zkreslení.
Flexibilní propojení - umožňuje bezproblémové propojení mezi třemi samostatnými sítěmi nebo napájecími kanály.
Ideální pro komplexní energetické systémy - podporuje potřeby pomocného napájení bez přídavných transformátorů.
Aplikace třívinuťových transformátorů:
Třívinuťové transformátory vynikají v komplexních energetických systémech a moderních energetických sítích, včetně:
Rozvodny a elektrárny - zajištění plynulé transformace napětí v přenosových a distribučních sítích.
Vysokonapěťové přenosové sítě - propojení různých napětí sítě nebo rozvoden.
Průmyslová zařízení potřebují vyhrazené pomocné zdroje napájení, jako je tovární osvětlení, řídicí systémy a napájení přístrojů.
Rozbočovače obnovitelných zdrojů energie - tam, kde větrná a solární zařízení a zařízení pro ukládání energie vyžadují stabilní výkon ve více napájecích sítích nebo připojeních k síti.
Projekty inteligentních sítí - zlepšení kvality energie a zvýšení odolnosti, aby bylo možné uspokojit budoucí požadavky na energii.
Výběr správného transformátoru pro vaši aplikaci
Výběr nejvhodnějšího transformátoru je zásadní technické rozhodnutí, které závisí na technických požadavcích projektu, poptávce po výkonu, složitosti systému a dlouhodobých provozních cílech. Při správné volbě mezi dvou- a třívinutými konstrukcemi transformátorů hrají roli faktory, jako je rozmanitost zatížení, prostředí instalace, cíle energetické účinnosti a budoucí rozšiřitelnost.
✅ Dvouvinuťové transformátory jsou ideální pro jednoduché rozvodné sítě a představují jednoduché a robustní řešení pro většinu běžných aplikací. Tyto transformátory jsou navrženy s jedním primárním a jedním sekundárním vinutím a vynikají v jednostupňových převodech napětí - zvyšují nebo snižují napětí podle potřeb komerčních budov, továren, napájecích sítí a obytných komplexů. Díky nákladově efektivní konstrukci snižují náklady na plochu a instalaci a zároveň poskytují osvědčený výkon v široké škále sítí středního a nízkého napětí, včetně průmyslových procesních zařízení, osvětlovacích systémů, instalací HVAC, připojení obnovitelných zdrojů energie a samostatných generátorů.
✅ Transformátory se třemi vinutími nabízejí větší flexibilitu pro složitější nebo rychle se vyvíjející energetické systémy. Díky třem nezávislým vinutím - primárnímu, sekundárnímu a terciárnímu - mohou efektivně napájet více zátěží nebo se propojit s různými segmenty sítě při různých napětích. Díky tomu jsou optimální volbou pro konstrukce rozvoden s více výstupy, integraci inteligentních sítí, průmyslové elektrárny s velkým výkonem a uzly obnovitelných zdrojů energie, kde je třeba dodávat stabilní výkon do různých napájecích zdrojů, pomocných zařízení nebo záložních napájecích sítí. Díky své vícenapěťové schopnosti pomáhají třívinuťové transformátory také vyrovnávat nesymetrické zátěže, snižovat harmonické zkreslení, optimalizovat korekci účiníku a zvyšovat celkovou spolehlivost systému - často tak lze eliminovat další transformátorové jednotky a zjednodušit architekturu napájení.
Závěr
V moderní elektrické infrastruktuře hrají zásadní roli jak dvouvinuté, tak třívinuté transformátory. Dvouvinuťové transformátory představují efektivní a osvědčené řešení pro většinu základních potřeb v oblasti přeměny a distribuce elektrické energie - zejména v komerčním a lehkém průmyslu. Třívinutové transformátory naproti tomu nabízejí sofistikovanější, na budoucnost připravenou variantu pro rozsáhlé sítě nebo sítě s více přívody, které umožňují lepší sdílení energie, vyšší odolnost systému a bezproblémovou integraci obnovitelných zdrojů energie, jako jsou např. solární farmy, větrné parky a řešení pro skladování energie.
Pečlivým vyhodnocením požadavků na systém - včetně kapacity napájení, rozmanitosti napětí, topologie sítě a profilu zátěže - můžete učinit informované rozhodnutí, které zvýší technický výkon i ekonomickou hodnotu. Výběr správného transformátoru nejen zvyšuje bezpečnost, účinnost a životnost vaší elektrické sítě, ale také podporuje dlouhodobou škálovatelnost celé vaší elektrické infrastruktury.
Proč si vybrat Evernew Transformer?
Společnost Evernew Transformer, jeden z nejlepších čínských výrobců výkonových transformátorů, se specializuje na zakázkové dvou- a třívinuťové transformátory pro různé průmyslové aplikace, aplikace pro veřejné služby a obnovitelné zdroje energie. Naše výrobky mají certifikace CE, UL a GOST, které zajišťují prvotřídní kvalitu a shodu na světových trzích. Ať už potřebujete standardní řešení nebo plně přizpůsobené konstrukce, které vyhovují vašim jedinečným energetickým požadavkům, nabízíme konkurenceschopné ceny, efektivní výrobu a rychlé dodání.
Spojte se s námi
Jste připraveni modernizovat svou elektrickou infrastrukturu pomocí transformátoru na míru?
Kontaktujte společnost Evernew Transformer ještě dnes - nechte náš tým zkušených inženýrů, aby vám pomohli navrhnout nejúčinnější, nejbezpečnější a nejhospodárnější výkonový transformátor pro vaši aplikaci.